Langchain: OutputParser
Having a model returning output that matches a specific schema is useful for many reasons. It can make the output more predictable and processable, and also can be used for downstream systems integration. For exampple, we can extract data from text to insert into a database.
In LangChain, we have two main approaches to parse structured outputs. In this blog, we will cover them in details.
Implementing with with_structured_output
This approach only works with models that provide native APIs for structured outputs like tool calling or JSON mode. The list could be found here.
The function will take a schema as input which specfics the name, types, and descriptions of the descried output attributes. The schema could be defined by Pydantic, TypeScript or JSON Schema. The most advanced one is Pydantic which can enable the validation of the arguments.
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4")
class ResponseFormatter(BaseModel):
"""Response formatter for the question"""
answer: str = Field(description="Main answer to the question")
confidence: float = Field(description="Confidence score between 0 and 1")
sources: list[str] = Field(description="Reference sources used")
structured_llm = model.with_structured_output(ResponseFormatter)
response = structured_llm.invoke("What is LangChain?")
print(response)
You can also use multiple schemas to parse the output. The LLM will automatically determine which schema to use.
from typing import Union
from typing import Optional
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
class QuestionResponse(BaseModel):
"""Respond in a structured manner with the answer and confidence score"""
answer: str = Field(description="Main answer to the question")
confidence: Optional[float] = Field(description="Confidence score between 0 and 1")
class JokeResponse(BaseModel):
"""Joke to tell user."""
setup: str = Field(description="The setup of the joke")
punchline: str = Field(description="The punchline to the joke")
rating: Optional[int] = Field(
default=None, description="How funny the joke is, from 1 to 10"
)
class FinalResponse(BaseModel):
final_output: Union[JokeResponse, QuestionResponse]
structured_llm = model.with_structured_output(FinalResponse)
print(structured_llm.invoke("What is deep learning?"))
print(structured_llm.invoke("Tell me a joke about cats"))
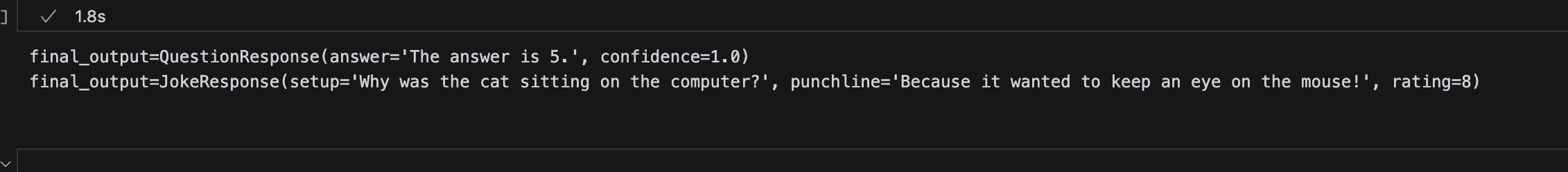
As you can see, the LLM will return the output based on the schema that matches the input. The swithc is enabled by the description and schema that we provided. This is the also the best practice to use the structured output methods. At the end, we will summarize it.
This method takes a schema as input which specifies the names, types, and descriptions of the desired output attributes.
As we mentioned, the with_structured_output method only works with models that provide native APIs for structured outputs. If you want to use it with other models, we should directly prompt the model to use a specific schema and use the output parser to parse the structuredoutput from the raw output. The following two approaches both belong to this category.
Implementing with OutputParser
OutputParser are classes that help to parse raw outputs from the LLM. The most common one is PydanticOutputParser which is used to parse the output from the LLM into a Pydantic object. In LangChain, for each output parser, there are two main methods:
get_format_instructions(): This method returns the format instructions for the output parser.parse(text: str): This method parses the raw output from the LLM into the desired format.
There is also one optional method Prase with prompt which take the raw output from the LLM and the prompt that generated such raw output as inputs and return the parsed output.
Here, we will use PydanticOutputParser to parse the output from the LLM into a Pydantic object.
from typing import List
from langchain_core.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class Person(BaseModel):
"""Information about a person."""
name: str = Field(..., description="The name of the person")
height_in_meters: float = Field(
..., description="The height of the person expressed in meters."
)
class People(BaseModel):
"""Identifying information about all people in a text."""
people: List[Person]
# Set up a parser
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=People)
# Pompt
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate(
[
(
"system",
"Answer the user query. Wrap the output in `json` tags\n{format_instructions}",
),
("human", "{query}"),
]
).partial(format_instructions=parser.get_format_instructions())
query = "Anna is 23 years old and she is 6 feet tall"
print(prompt.invoke({"query": query}).to_string())
The output here is:
System: Answer the user query. Wrap the output in `json` tags
The output should be formatted as a JSON instance that conforms to the JSON schema below.
As an example, for the schema {"properties": {"foo": {"title": "Foo", "description": "a list of strings", "type": "array", "items": {"type": "string"}}}, "required": ["foo"]}
the object {"foo": ["bar", "baz"]} is a well-formatted instance of the schema. The object {"properties": {"foo": ["bar", "baz"]}} is not well-formatted.
Here is the output schema:
{"$defs": {"Person": {"description": "Information about a person.", "properties": {"name": {"description": "The name of the person", "title": "Name", "type": "string"}, "height_in_meters": {"description": "The height of the person expressed in meters.", "title": "Height In Meters", "type": "number"}}, "required": ["name", "height_in_meters"], "title": "Person", "type": "object"}}, "description": "Identifying information about all people in a text.", "properties": {"people": {"items": {"$ref": "#/$defs/Person"}, "title": "People", "type": "array"}}, "required": ["people"]}
Human: Anna is 23 years old and she is 6 feet tall
You can see this is the prompt that we sent to the model. From the naming of variable and the description, those key information are populated into the prompt directly via the method get_format_instructions
Than, we can invoke the model with the prompt and get the structured output.
chain = prompt | model | parser
result = chain.invoke({"query": query})
result_dict = result.model_dump()
print(result)
print(result_dict)
The results are given below:
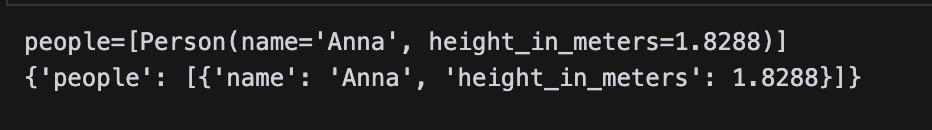
The model_dump() method is used to convert the Pydantic object into a dictionary.
Best Practices with Structured Outputs
- Design clear and concise schema: clear and concise schema is important for the model to understand the output and for the parser to parse the output. We should consider all possible fields and their types.
- Use descriptive and specific field names: field names should be self-explanatory and consistent with your application’s naming conventions.
- Provide detailed descriptions for each field: clear descriptions for each field should be provided to guide the LLM.
- Keep it simple: Start with simple structures and gradually increase complexity as needed.
References
- Langchain (2024). Langchain Tutorials. Langchain Documentation . [link]
